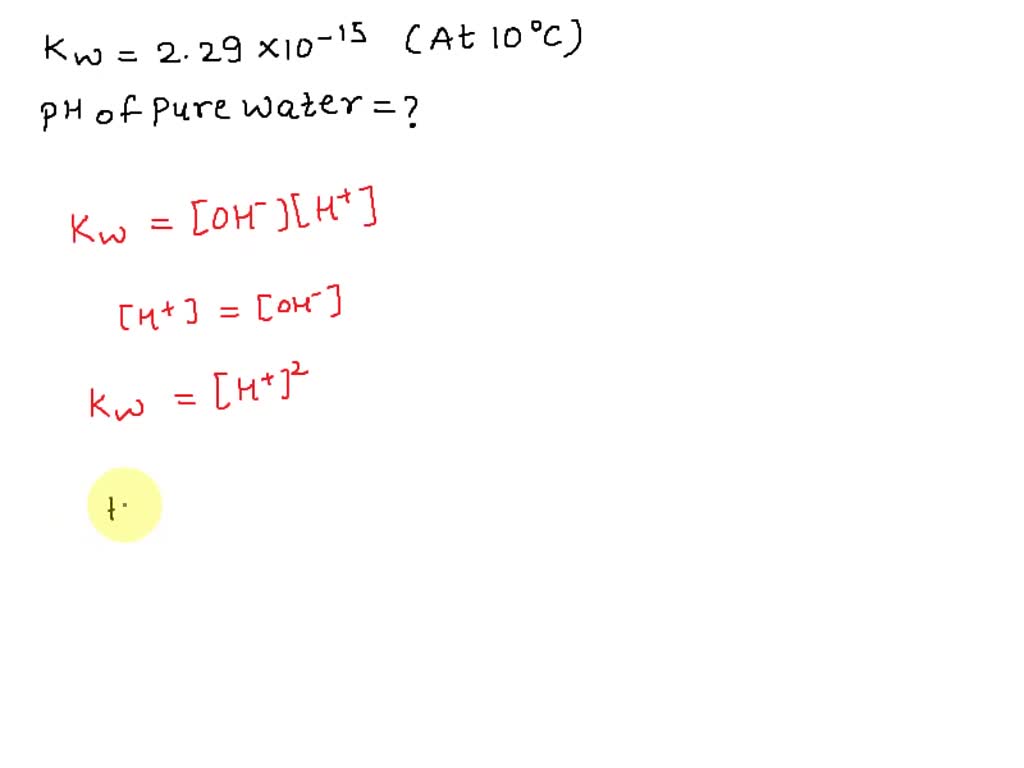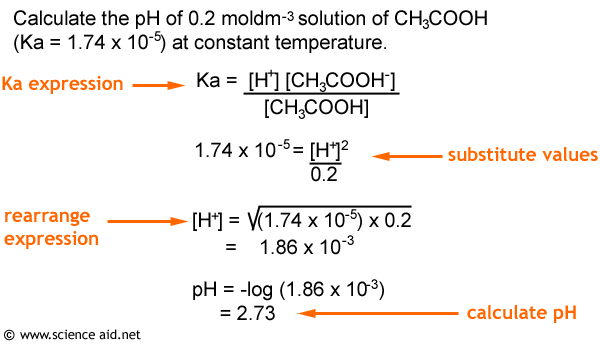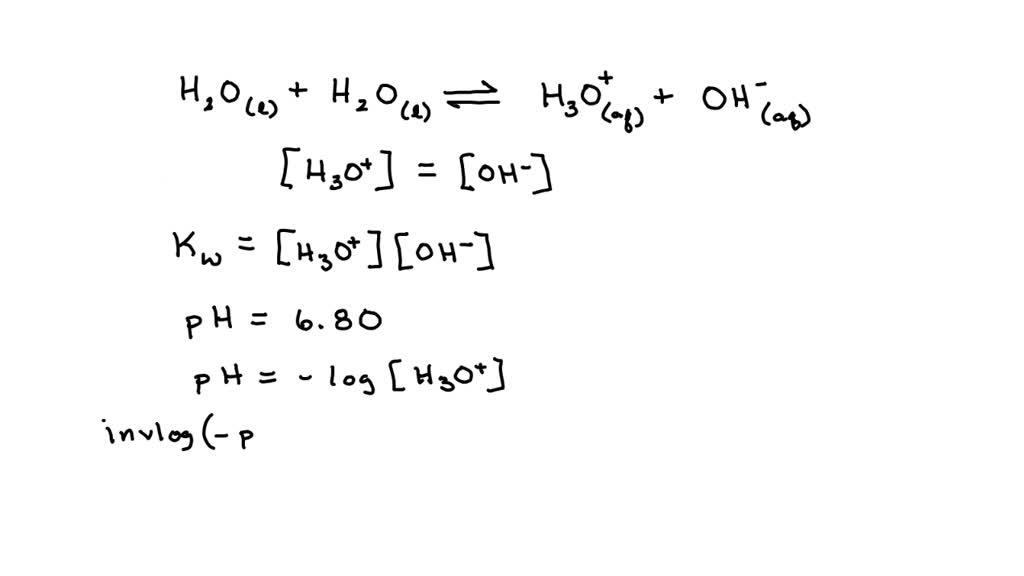
SOLVED: If the pH of pure water is 6.80 at 37 C, determine the value of KW at this temperature (it would be more relevant in medical applications that the value at 25 C).

AutoIonization of Water, Ion Product Constant - Kw, Calculating H3O+, OH-, and pH Using Ice Tables - YouTube
![SOLVED: At 50°C, the value of Kw is 5.47 x 10^-14. a) Calculate the [H+] and [OH-] in pure water at 50°C. [H+] M [OH-] M b) What is the pH of SOLVED: At 50°C, the value of Kw is 5.47 x 10^-14. a) Calculate the [H+] and [OH-] in pure water at 50°C. [H+] M [OH-] M b) What is the pH of](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_previews/ed96ab60-48fb-4213-8fd0-3c129172f46d_large.jpg)
SOLVED: At 50°C, the value of Kw is 5.47 x 10^-14. a) Calculate the [H+] and [OH-] in pure water at 50°C. [H+] M [OH-] M b) What is the pH of
The ionization constant for water (Kw) is 9.311 × 10−14 at 60 °C. What is the [H3O+], [OH−], pH, and pOH for pure water at 60 °C? Thanks. - TopScience - Quora
![PPT - Definition pH and pOH. Given pH, pOH, [H 3 O + ] or [OH¯], calculate the remaining values. PowerPoint Presentation - ID:5054819 PPT - Definition pH and pOH. Given pH, pOH, [H 3 O + ] or [OH¯], calculate the remaining values. PowerPoint Presentation - ID:5054819](https://image2.slideserve.com/5054819/slide13-l.jpg)
PPT - Definition pH and pOH. Given pH, pOH, [H 3 O + ] or [OH¯], calculate the remaining values. PowerPoint Presentation - ID:5054819
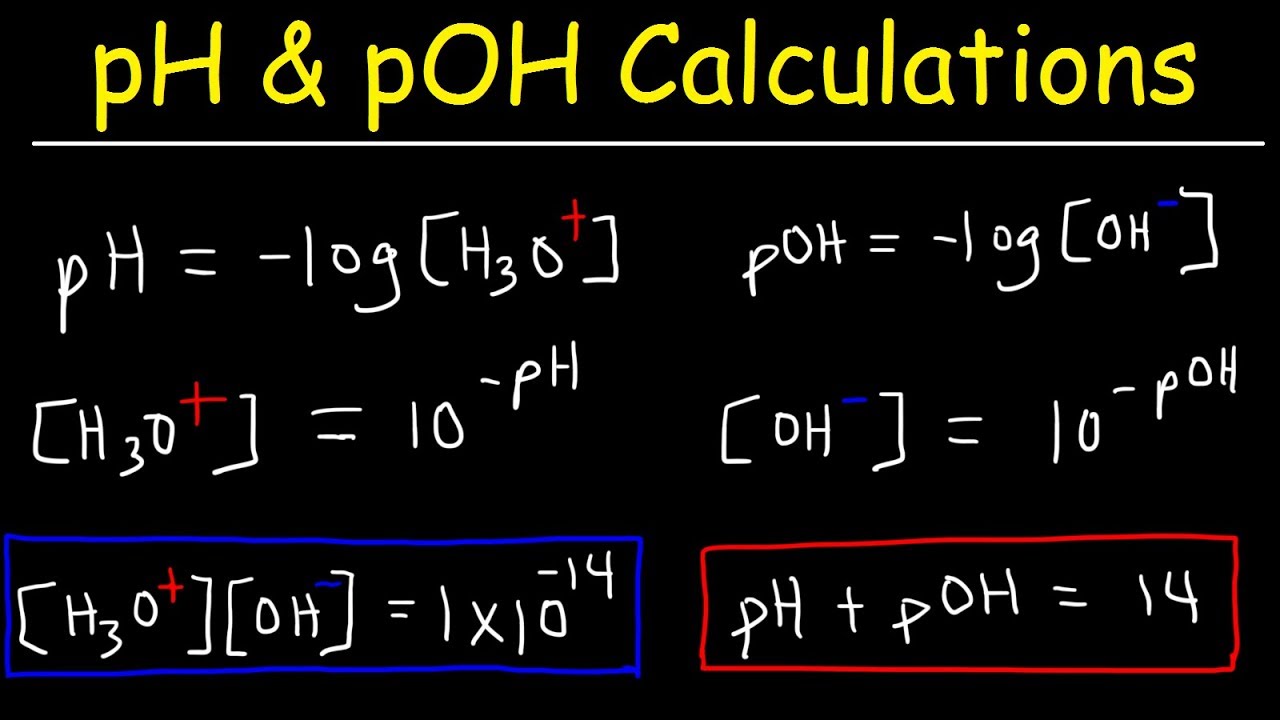
pH, pOH, H3O+, OH-, Kw, Ka, Kb, pKa, and pKb Basic Calculations -Acids and Bases Chemistry Problems - YouTube

pH from Base concentration and Ionic Product of Water calculation Workthrough - A2 Chemistry - YouTube
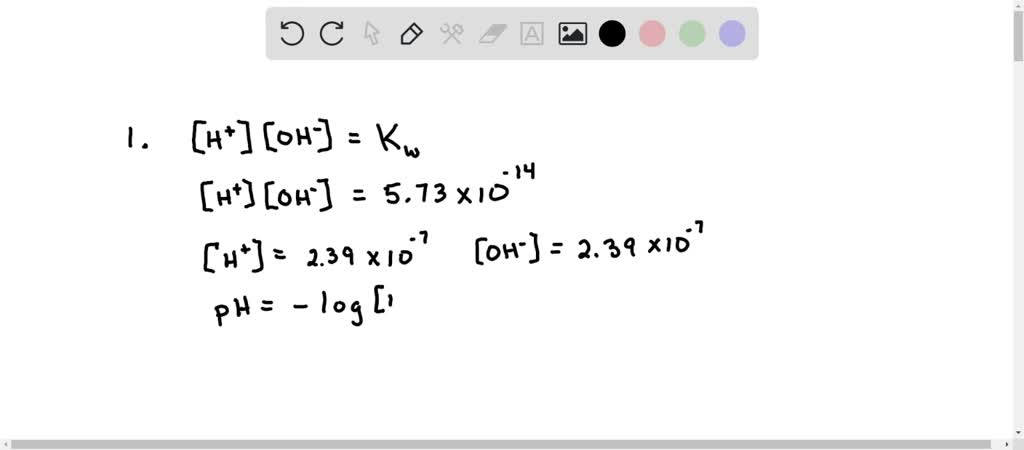
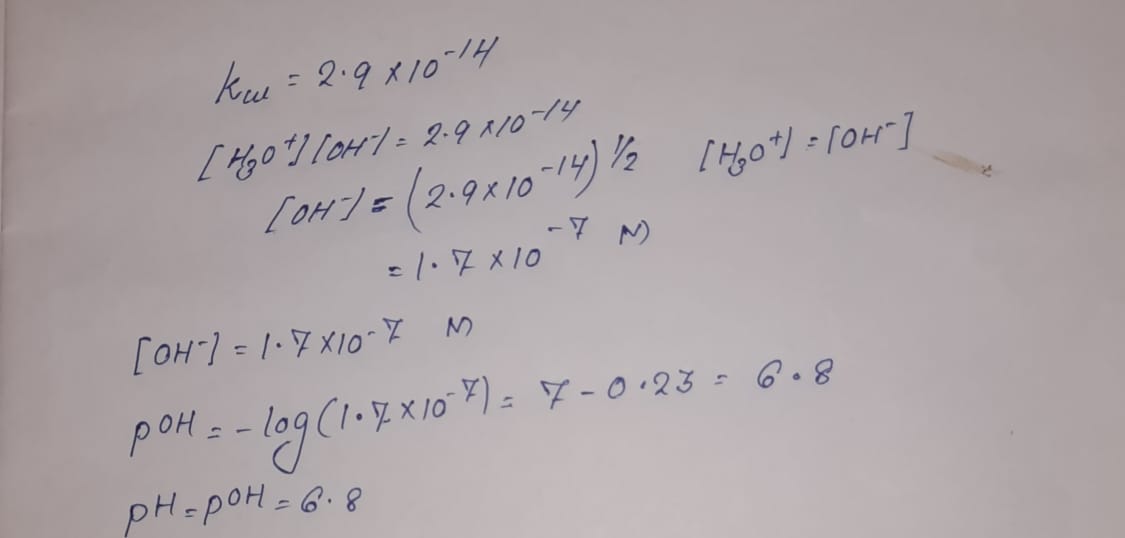



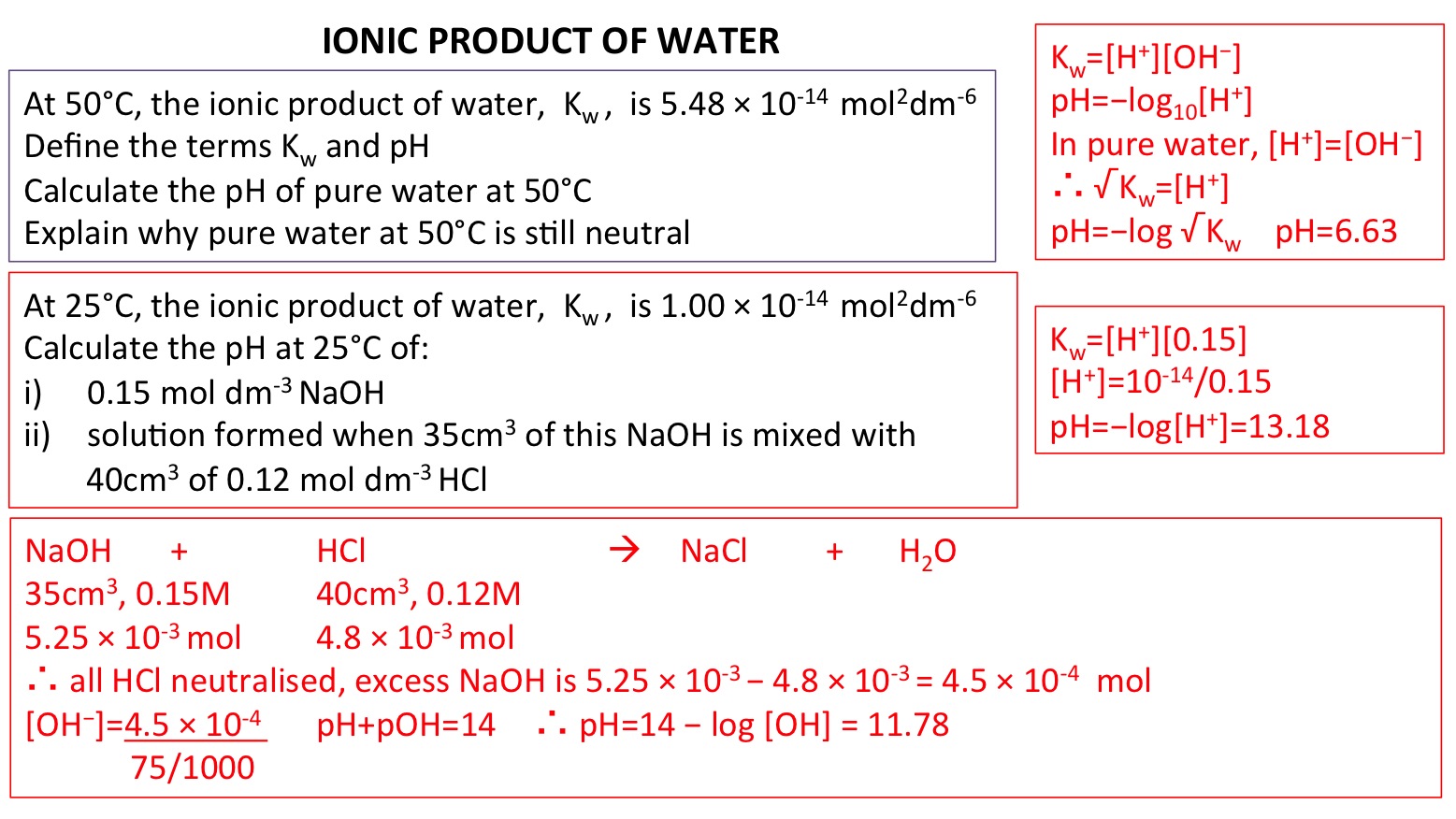
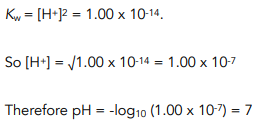



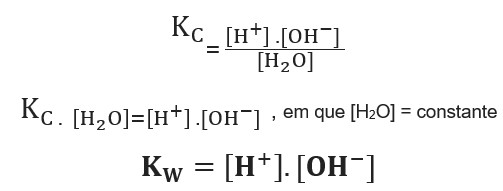

![Acids and Bases Part 4: Kw and Calculation of [H+] and [OH-] - YouTube Acids and Bases Part 4: Kw and Calculation of [H+] and [OH-] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/IvP_PxetNUw/maxresdefault.jpg)